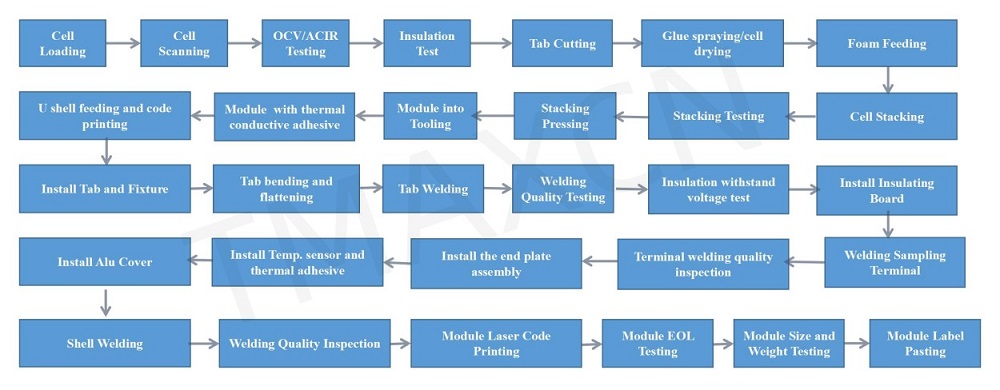
A lithium battery Assembly machine is a production facility designed for the manufacturing of lithium-ion battery cells. This line involves a series of sequential processes that transform raw materials into finished lithium battery pilot machine suitable for use in various applications, including electric vehicles, consumer electronics, and energy storage systems. Here's a detailed breakdown of the key stages in a lithium cell fabrication line:
Materials Processing and Preparation:
Raw Material Handling: Electrode materials, electrolytes, separators, and other components are processed and prepared for the manufacturing process.
Mixing and Coating: Electrode materials are mixed, coated onto current collectors, and calendared to achieve the desired thickness.
Electrode Winding or Stacking:
Winding (Cylindrical Cells) or Stacking (Prismatic Cells): Electrode-coated current collectors are either wound into a cylindrical shape or stacked to form the electrode assembly.
Assembly:
Cell Stacking: Electrode assemblies are combined with separators and arranged in a specific configuration to form a complete cell.
Can Sealing (Cylindrical Cells) or Pouch Sealing (Pouch Cells): The assembled cells are enclosed in metal cans (for cylindrical cells) or sealed pouches (for pouch cells) to create a sealed unit.
Electrolyte Filling:
Electrolyte Injection: The sealed cells undergo a process where electrolyte is injected to facilitate ion transport within the cell.
Formation Process:
Charge and Discharge Cycling: Cells undergo controlled charge and discharge cycles in a formation process to stabilize and activate them.
Quality Control and Testing:
Visual Inspection: Automated systems inspect the cells for visual defects or irregularities.
Performance Testing: Cells undergo testing for capacity, voltage, internal resistance, and other performance parameters.
Safety Testing: Evaluation of safety features, including response to overcharging, short circuits, and thermal conditions.
Tab Welding (for Cylindrical Cells):
Tab Welding Machines: Metal tabs are welded to the electrodes for external electrical connections.
Labeling and Packaging:
Labeling: Cells are labeled with essential information, including specifications, safety warnings, and barcodes.
Packaging: Finished cells are packaged for transportation and distribution.
Research and Development (R&D):
Prototyping: Dedicated facilities for developing and testing prototype cells with innovative designs and materials.
Process Optimization: Continuous efforts to optimize manufacturing processes through research and development initiatives.
Data Collection and Analysis:
Integrated Data Logging Systems: Comprehensive software and tools for collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data from various stages of the manufacturing process.
Automation and Advanced Technologies:
Robotics and Automation: Integration of automated systems and robotics to enhance precision, efficiency, and consistency.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Implementation of AI for quality control, process optimization, and predictive maintenance.
Scale-Up:
Capacity Expansion: Successful lithium battery pilot line undergo expansion to meet growing market demand.
Environmental Considerations:
Sustainability Practices: Adoption of sustainable and environmentally friendly manufacturing practices to minimize waste and energy consumption.
A well-established lithium cell fabrication line combines precision engineering, automation, and rigorous quality control to produce high-performance and reliable lithium-ion battery cells. Continuous innovation, adherence to safety standards, and environmental consciousness are integral aspects of the development and operation of such fabrication lines.
 fr
fr en
en de
de ru
ru es
es pt
pt ko
ko tr
tr pl
pl th
th







 réseau ipv6 pris en charge
réseau ipv6 pris en charge